Medicina: Neuropsicologia cognitiva
| English |
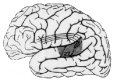
| wernicke’s aphasia |
  |
|
| Attestation |
3
|
| Part of speech |
Noun phrase
|
| Definition |
Fluent aphasia with frequent semantic (verbal) paraphasias. Language comprehension, naming and repetition are severely impaired.
Fluent aphasia with frequent semantic (verbal) paraphasias. Language comprehension and repetition are severely impaired. Naming is impaired, and in contrast to Broca’s aphasia, prompting provides little benefit. Lesions usually involve the posterior-superior portion of the dominant hemisphere temporal lobe. The lesions are generally vascular.
|
| Definition source |
Loring D. W. 1999
Loring D. W. 1999
|
| Context |
Direct observations of auditory comprehension deficiency reveal the primary symptoms of a Wernicke´s aphasia. Other symptoms of this disorder are the secondary effects of the primary breakdown; secondary effects in Wernicke´s aphasia include repetition failures, lack of awareness of jargon, reading deficits, and possibly, the jargon itself. Secondary symptoms appear because a single component of the cognitive basis for language function, however defined, interacts with all other components in the use of language.
|
| Context source |
Code 1989
|
| Figure source |
Ospedale Campo di Marte 2001
|
| Subject field |
Aphasia
|
| Sub-field (level 1) |
Aphasiology
|
| Sub-field (level 2) |
Clinical neuropsychology
|
| Sub-field (level 3) |
Aphasic syndromes
|
| Generic concept |
Fluent aphasia
|
| Related concept |
Conduction aphasia, Subcortical aphasia, Transcortical sensory aphasia, Amnesic aphasia
|
| it |
Afasia di Wernicke
|
| Reliability code |
3
|
|


