Medicina: Neuropsicologia cognitiva
| English |
| global aphasia |
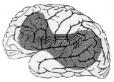  |
|
| Attestation |
3
|
| Part of speech |
Noun phrase
|
| Definition |
Nonfluent aphasia that involves nearly complete loss of all core linguistic functions including fluency, comprehension, repetition, reading and writing.
Nonfluent aphasia that involves nearly complete loss of all core linguistic functions including fluency, comprehension, repetition, reading, and writing. Large lesions involving Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area, as well as other perisylvian language regions, are generally found.
|
| Definition source |
Loring D. W. 1999
Loring D. W. 1999
|
| Context |
Some of the most severe instances of jargon and global aphasia in the Kertesz series (1979a) occurred in patients with ruptured middle cerebral aneurysms. In a study of recovery from acute aphasia in 21 young adults at least 6 months after closed head injury. Levin, Grossman, Sarwar, and Meyers (1981) reported that the 9 who recovered normal levels of language performance had mild diffuse brain injury.
|
| Context source |
Sarno 1991
|
| Figure source |
Ospedale Campo di Marte 2001
|
| Subject field |
Aphasia
|
| Sub-field (level 1) |
Aphasiology
|
| Sub-field (level 2) |
Clinical neuropsychology
|
| Sub-field (level 3) |
Aphasic syndromes
|
| Generic concept |
Nonfluent aphasia
|
| Related concept |
Broca’s aphasia, Transcortical motor aphasia
|
| it |
Afasia globale
|
| Reliability code |
3
|
|


