Medicina: Neuropsicologia cognitiva
| English |
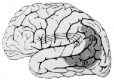
| anomic aphasia |
  |
|
| Attestation |
3
|
| Part of speech |
Noun phrase
|
| Definition |
Aphasia subtype characterized by impaired naming ability with circumlocutions, few paraphasias, good comprehension, fluent speech, and normal repetition.
Disorder in which patients indicate the understanding of a word´s meaning through the description of semantic features of form and function associated with the word. Verbal output may be fluent, but lacking in substantive words. Lesions usually involve the left hemisphere.
|
| Definition source |
Loring D. W. 1999
Code 1989
|
| Context |
Anomic errors were frequently associated with objects that bore a relation to the patient’s illness and frequently occurred during a period of disorientation, confabulation, and denial of illness. The authors observed that, in contrast to patients with classical anomic aphasia, patients exhibiting nonaphasic misnaming frequently showed no evidence of grouping for words in their spontaneous speech nor did their naming necessarily improve when correction was offered.
|
| Context source |
Sarno 1991
|
| Figure source |
Ospedale Campo di Marte 2001
|
| Synonym |
Amnesic aphasia, Amnestic aphasia
|
| Subject field |
Aphasia
|
| Sub-field (level 1) |
Aphasiology
|
| Sub-field (level 2) |
Clinical neuropsychology
|
| Sub-field (level 3) |
Aphasic syndromes
|
| Generic concept |
Fluent aphasia
|
| Related concept |
Wernicke’s aphasia, Transcortical sensory aphasia, Subcortical aphasia, Conduction aphasia
|
| it |
Afasia amnesica
|
| Reliability code |
3
|
|


