Medicina: Oncoematologia pediatrica: Leucemia linfoblastica acuta
| English |
| all |
  |
|
| Attestation |
3
|
| Variant |
acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute lymphoid leukemia, acute lymphogenous leukemia.
|
| Definition |
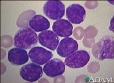
An acute rapidly progressive form of leukemia characterized by the presence in the blood and bone marrow of large numbers of unusually young (immature) white blood cells destined to become lymphocytes.These cells, called lymphoblasts, are rare items in blood under normal circumstances. It may follow an exposure to radioactive agents; but its true etiology is still unknown.
A rapidly progressive cancer that starts by the malignant transformation of a marrow lymphocyte. ALL is the most common form of childhood leukemia. The transformed, now malignant, cell multiplies and accumulates in the marrow as leukemic lymphoblasts. The lymphoblasts block normal blood cell-formation in the marrow, resulting in insufficient production of red cells, white cells and platelets. The specific chromosome and genic changes in the affected cells can be used to classify ALL. These findings can be used to determine the expected response of that type of ALL to treatment. The risk category of the ALL determined from the genic changes can affect the treatment applied.
|
| Definition source |
http://www.focusoncancer.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=13660&rd=1
http://www.leukemia.org/all_glossary.adp
|
| Context |
However, despite marked advances in therapy of childhood ALL, the probability of event-free survival (EFS) for infants is approximately 35% only, irrespective of different treatment protocols.
|
| Context source |
En09
|
| Figure source |
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/imagepage/1221.htm
|
| Synonym |
acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute lymphoid leukemia, acute lymphogenous leukemia.
|
| Subject field |
Pediatric Oncohematology
|
| Generic concept |
acute leukemia
|
| Specific concept |
B-lineage ALL, T-lineage ALL
|
| de |
ALL
|
| it |
LLA
|
| Reliability code |
3
|
|


